AUTOCARE WITH DAMILARE: BRAKE SYSTEMS
Autocare with Damilare
Brake System
Brakes are one of the most important control components of a vehicle.
They are required to stop the vehicle within the smallest possible distance and this is done by converting the kinetic energy of the wheels into the heat energy which is dissipated into the atmosphere.
Requirements of A Good Braking System
(i) To stop the vehicle in the shortest possible distance and time.
(ii) To control the vehicle speed while moving on plain roads and hills.
(iii) To work equally well on fair and bad roads.
(iv) To ensure that the pedal effort applied by the driver is not much, thereby reducing the inconvenience
for the driver.
(v) To work efficiently in all weathers
(vi) It should have very few wearing parts.
(vii) It should require little maintenance.
(viii) Brake, when applied should not disturb the steering geometry
(ix) There should be minimum sound when brake is applied.
Types of Brake
1. Foot Brake: Foot brake is one of the most common brake systems operated by the foot pedal. When pressure is applied to the foot pedal, the vehicle
stops. Pedal force applied by the driver is further multiplied and sent to the braking drum or disc either by mechanical linkages or by hydraulic
pressure which in turn causes braking. It is also known as a service brake.
2. Hand Brake: Hand brakes are usually used for stable parking of the vehicle either a on flat road or slope. They are also called parking brakes. Hand brakes are connected to the brake mechanism directly and the other end is operated by the driver. This type of brake is also known as emergency brake as it is independent of the main service brake.
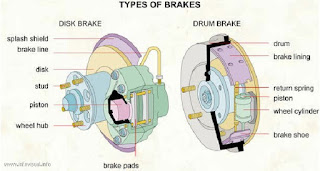
3. Drum Brakes or Internal Expanding Brakes: Drum brakes are usually used as rear brakes in most automobiles, which utilises the friction between the drum and the brake shoes to stop the vehicle. This type of brake is fitted in automobile light vehicle, such as car and light
trucks. These brakes have a two shoe, the left hand shoe is known as a primary shoe and the right hand shoe is known as trailing shoe. Shoes are fitted in the drum. The friction between the shoes and the drum produces the braking torque and reduces the
speed of the drum so that the vehicle stop.
4. Disc Brake or External Contracting Brakes: It is the type of braking system in which instead of a drum assembly a disc rotor is attached to the hub of the wheel in such a fashion that it rotates with the wheel. This disc rotor is clamped in between the caliper which is rigidly fixed with the knuckle or upright of the vehicle. When brakes are applied the actuation mechanism contracts the attached brake shoes which in turn make the frictional contact with the rotating disc rotor and cause the stopping of a vehicle. An external contracting brake is used for only parking purpose as well as used to
operate in flour mills, various types of electrical components, etc.
5. Mechanical Brake: This brake system has an inbuilt mechanical device for absorbing energy from a moving system. Mechanical brake is a cable
pull system, which consists of rim-like brakes just arranged in a different way.
6. Power Brake: Power brake system is a combination of the mechanical components to multiply the force applied to the brake pedal by the driver to stop the vehicle. In a power brake
system we mainly use the vacuum booster and master cylinder, brake calipers, drum brake, etc.
These braking systems are designed to reduce the effort required to depress the brake pedal when stopping a vehicle.
7. Vacuum Brake: It is the conventional type of braking system in which vacuum inside the brake lines causes brake pads to move, which in turn finally stop or deaccelerate the vehicle. This type
of brake is mainly used in railways in place of air brakes. This brake can remove the kinetic energy and convert it into a form of heat. The conversion is usually done by applying a contact material to the rotating wheel attached to the axles. Vacuum brakes are cheaper than air brakes but are less safe than air brakes.
8. Air Brake: Air brake system is a very advanced braking system. It is generally used in very heavy vehicles like buses and trucks. It is the type of braking system in which the atmospheric air through compressors and valves is used to transmit brake pedal force from brake pedal to the final drum or disc rotor. Air brakes generate higher brake force than hydraulic brake which
is the need of the heavy vehicle. High-end cars these days are using air brake systems due to its effectiveness and fail proof ability.
9. Hydraulic Brakes: A hydraulic braking system transmits brake-pedal force to the wheel brakes through pressurised fluid, converting the fluid pressure into useful work of braking at the wheels. The brake pedal relays the driver’s foot effort to the master-cylinder piston, which compresses the brake fluid. This fluid pressure is equally transmitted throughout the fluid to the front disc-caliper pistons and to the rear wheel-cylinder pistons. The pressure on a liquid is called hydraulic pressure. The brakes which are operated by means of hydraulic pressure are called hydraulic brakes.
10. Anti‑lock Braking System: Anti-lock Braking System prevents the wheels from locking or skidding. The anti-lock braking (ABS) system is a component that ensures passenger safety by stopping the vehicle in adverse conditions, like stopping very quickly or if the road is slippery. To simplify it, the ABS prevents the wheels of the vehicle from locking up and causing you to skid out of control.
11. Electric Brake: It is the type of braking used in electric vehicle. Electric brakes use electrical motors which are the main source of power in electric vehicles. Electric brakes or secondary
shoe are similar to the drum brakes in an automobile. Electric brakes are actuated by an electromagnet.





Comments
Post a Comment